Our current RPM spec file includes _all_ of our library dependencies as statically listed `Requires:` lines. This, in turn, requires a very large number of conditionals in the dependencies to account for package naming differences between RPM distros, and also makes it a pain in the arse to port the spec file to work with new releases of existing distros. This changes the spec file to just use the automatic `Requires:` generation functionality that's already included in the RPM build process. The net effect is that the spec file ends up much cleaner, and it works just about anywhere with minimal modification., as well as us not having to track anything but build dependencies manually. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| .travis | ||
| aclk | ||
| backends | ||
| build | ||
| build_external | ||
| claim | ||
| cli | ||
| collectors | ||
| contrib | ||
| daemon | ||
| database | ||
| diagrams | ||
| docs | ||
| exporting | ||
| health | ||
| libnetdata | ||
| packaging | ||
| parser | ||
| registry | ||
| spawn | ||
| streaming | ||
| system | ||
| tests | ||
| web | ||
| .clang-format | ||
| .codacy.yml | ||
| .codeclimate.yml | ||
| .csslintrc | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .eslintignore | ||
| .eslintrc | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .lgtm.yml | ||
| .mlc_config.json | ||
| .remarkignore | ||
| .remarkrc.js | ||
| .squash.yml | ||
| .travis.yml | ||
| .yamllint.yml | ||
| BREAKING_CHANGES.md | ||
| BUILD.md | ||
| CHANGELOG.md | ||
| CMakeLists.txt | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTORS.md | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| Dockerfile.test | ||
| HISTORICAL_CHANGELOG.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile.am | ||
| README.md | ||
| REDISTRIBUTED.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| build-artifacts.sh | ||
| configs.signatures | ||
| configure.ac | ||
| coverity-scan.sh | ||
| cppcheck.sh | ||
| netdata-installer.sh | ||
| netdata.cppcheck | ||
| netdata.spec.in | ||
| package-lock.json | ||
| package.json | ||
README.md
Netdata 



Netdata is distributed, real-time performance and health monitoring for systems and applications. It is a highly-optimized monitoring agent you install on all your systems and containers.
Netdata provides unparalleled insights, in real-time, of everything happening on the systems it's running on (including web servers, databases, applications), using highly interactive web dashboards.
A highly-efficient database stores long-term historical metrics for days, weeks, or months, all at 1-second granularity. Run this long-term storage autonomously, or integrate Netdata with your existing monitoring toolchains (Prometheus, Graphite, OpenTSDB, Kafka, Grafana, and more).
Netdata is fast and efficient, designed to permanently run on all systems (physical and virtual servers, containers, IoT devices), without disrupting their core function.
Netdata is free, open-source software and it currently runs on Linux, FreeBSD, and macOS, along with other systems derived from them, such as Kubernetes and Docker.
Netdata is not hosted by the CNCF but is the fourth most starred open-source project in the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) landscape.
People get addicted to Netdata. Once you use it on your systems, there is no going back! You've been warned...
Contents
- What does it look like? - Take a quick tour through the dashboard
- Our userbase - Enterprises we help monitor and our userbase
- Quickstart - How to try it now on your systems
- Why Netdata - Why people love Netdata and how it compares with other solutions
- News - The latest news about Netdata
- How Netdata works - A high-level diagram of how Netdata works
- Infographic - Everything about Netdata in a single graphic
- Features - How you'll use Netdata on your systems
- Visualization - Learn about visual anomaly detection
- What Netdata monitors - See which apps/services Netdata auto-detects
- Documentation - Read the documentation
- Community - Discuss Netdata with others and get support
- License - Check Netdata's licencing
- Is it any good? - Yes.
- Is it awesome? - Yes.
What does it look like?
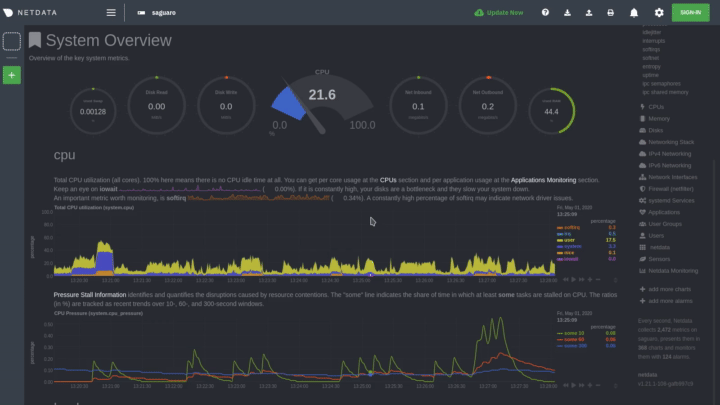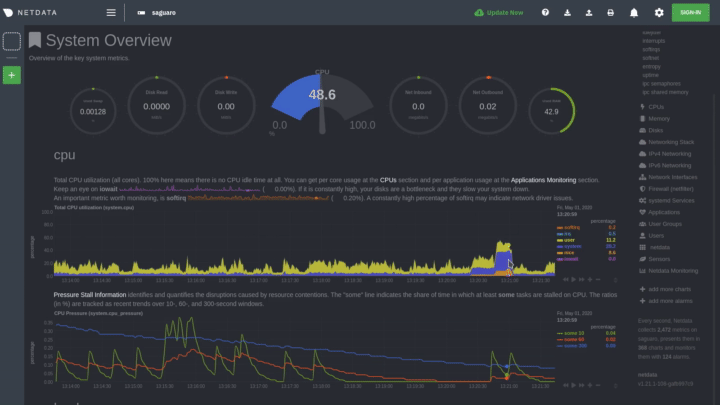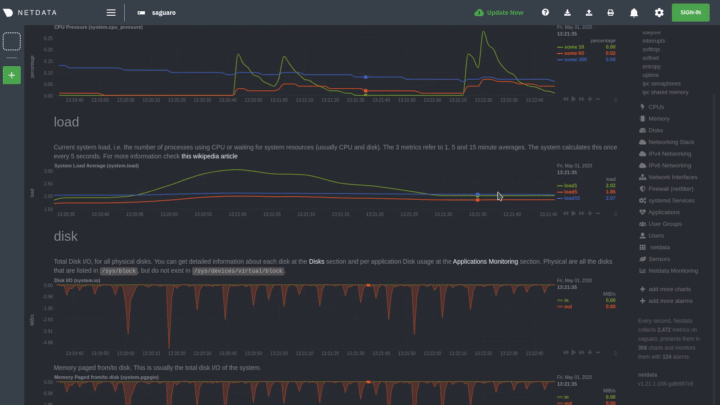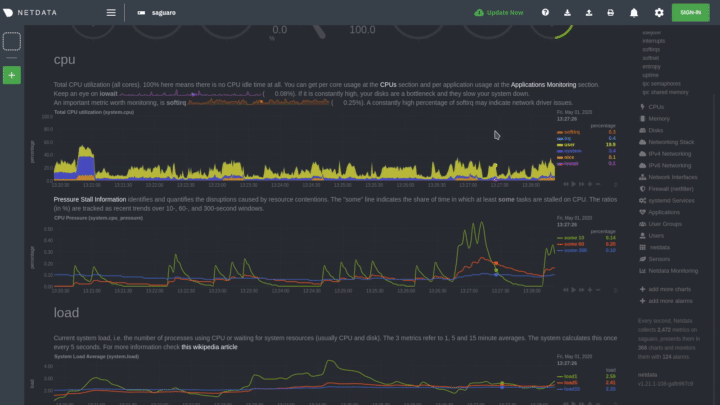
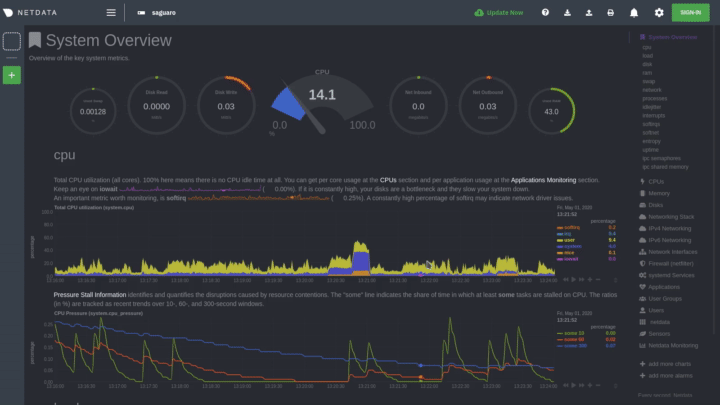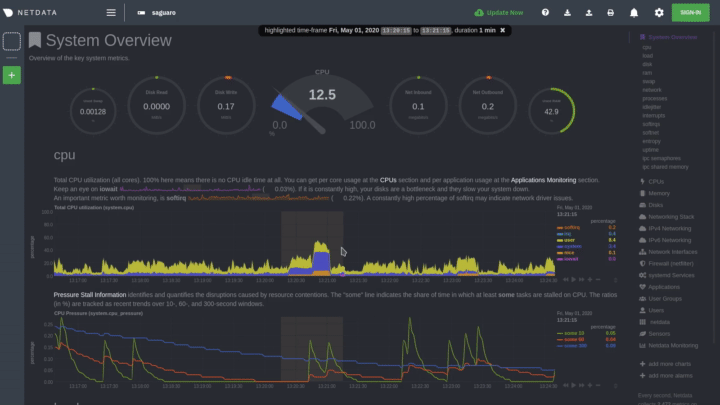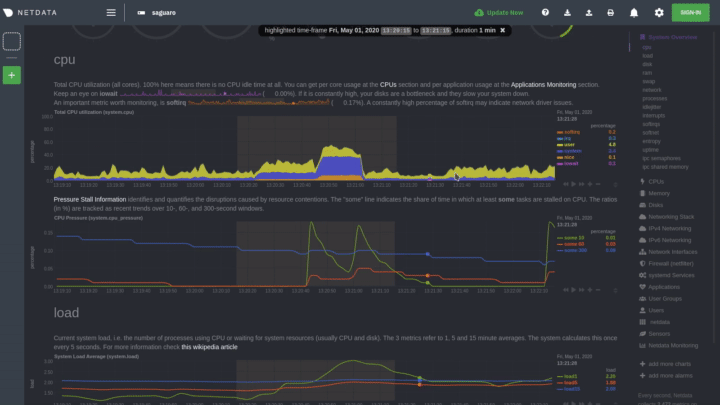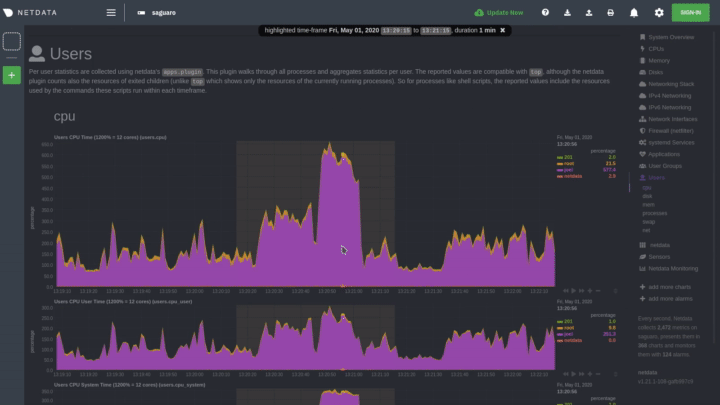
The following animated GIF shows the top part of a typical Netdata dashboard.
A typical Netdata dashboard, in 1:1 timing. Charts can be panned by dragging them, zoomed in/out with
SHIFT+mouse wheel, an area can be selected for zoom-in withSHIFT+mouse selection. Netdata is highly interactive, real-time, and optimized to get the work done!
Want to try Netdata before you install? See our live demo.
User base
Netdata is used by hundreds of thousands of users all over the world. Check our GitHub watchers list. You will find people working for Amazon, Atos, Baidu, Cisco Systems, Citrix, Deutsche Telekom, DigitalOcean, Elastic, EPAM Systems, Ericsson, Google, Groupon, Hortonworks, HP, Huawei, IBM, Microsoft, NewRelic, Nvidia, Red Hat, SAP, Selectel, TicketMaster, Vimeo, and many more!
Docker pulls
We provide Docker images for the most common architectures. These are statistics reported by Docker Hub:
Registry
When you install multiple Netdata, they are integrated into one distributed application, via a Netdata registry. This is a web browser feature and it allows us to count the number of unique users and unique Netdata servers installed. The following information comes from the global public Netdata registry we run:
Quickstart
To install Netdata from source on any Linux system (physical, virtual, container, IoT, edge), including all dependencies required to connect to Netdata Cloud, and get automatic nightly updates, run the following as your normal user:
# make sure you run `bash` for your shell
bash
# install Netdata directly from GitHub source
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)
Starting with v1.12, Netdata collects anonymous usage information by default and sends it to Google Analytics. Read about the information collected, and learn how to-opt, on our anonymous statistics page.
The usage statistics are vital for us, as we use them to discover bugs and prioritize new features. We thank you for actively contributing to Netdata's future.
To learn more about the pros and cons of using nightly vs. stable releases, see our notice about the two options.
The above command will:
- Install any required packages on your system (it will ask you to confirm before doing so)
- Compile it, install it, and start it.
More installation methods and additional options can be found at the installation page.
To try Netdata in a Docker container, run this:
docker run -d --name=netdata \
-p 19999:19999 \
-v netdatalib:/var/lib/netdata \
-v netdatacache:/var/cache/netdata \
-v /etc/passwd:/host/etc/passwd:ro \
-v /etc/group:/host/etc/group:ro \
-v /proc:/host/proc:ro \
-v /sys:/host/sys:ro \
-v /etc/os-release:/host/etc/os-release:ro \
--restart unless-stopped \
--cap-add SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt apparmor=unconfined \
netdata/netdata
For more information about running Netdata in Docker, check the docker installation page.
From Netdata v1.12 and above, anonymous usage information is collected by default and sent to Google Analytics. To read more about the information collected and how to opt-out, check the anonymous statistics page.
Why Netdata
Netdata has a quite different approach to monitoring.
Netdata is a monitoring agent you install on all your systems. It is:
- A metrics collector for system and application metrics (including web servers, databases, containers, and much more),
- A long-term metrics database that stores recent metrics in memory and "spills" historical metrics to disk for efficient long-term storage,
- A super fast, interactive, and modern metrics visualizer optimized for anomaly detection,
- And an alarms notification engine for detecting performance and availability issues.
All the above, are packaged together in a very flexible, extremely modular, distributed application.
This is how Netdata compares to other monitoring solutions:
| Netdata | others (open-source and commercial) |
|---|---|
| High resolution metrics (1s granularity) | Low resolution metrics (10s granularity at best) |
| Monitors everything, thousands of metrics per node | Monitor just a few metrics |
| UI is super fast, optimized for anomaly detection | UI is good for just an abstract view |
| Long-term, autonomous storage at one-second granularity | Centralized metrics in an expensive data lake at 10s granularity |
| Meaningful presentation, to help you understand the metrics | You have to know the metrics before you start |
| Install and get results immediately | Long preparation is required to get any useful results |
| Use it for troubleshooting performance problems | Use them to get statistics of past performance |
| Kills the console for tracing performance issues | The console is always required for troubleshooting |
| Requires zero dedicated resources | Require large dedicated resources |
Netdata is open-source, free, super fast, very easy, completely open, extremely efficient, flexible and integrate-able.
It has been designed by system administrators, DevOps engineers, and developers for to not just visualize metrics, but also troubleshoot complex performance problems.
News
August 10, 2020- Netdata v1.24.0 released!
The v1.24.0 release of the Netdata Agent brings enhancements to the breadth of metrics we collect with a new Prometheus/OpenMetrics collector and enhanced storage and querying with a new multi-host database mode.
July 16, 2020 - Netdata v1.23.2 released!
Release v1.23.2 of the Netdata Agent is a patch for one significant issue.
PR #9491 fixed a buffer overrun vulnerability in Netdata's JSON parsing code. This vulnerability could be used to crash Agents remotely, and in some circumstances, could be used in an arbitrary code execution (ACE) exploit.
We strongly encourage all Netdata users to update their nodes to v1.23.2 as soon as possible.
This release also contains additional bug fixes and improvements.
July 1, 2020 - Netdata v1.23.1 released!
Release v1.23.1 of the Netdata Agent is a patch for two significant issues.
PR #9436 fixed an issue where dimensions were marked obsolete and archived simultaneously, which caused segmentation faults. We're grateful to marioem, who first reported the issue, and other members of the Netdata community who contributed their insights and valuable log information, which we used to diagnose and fix the bug.
PR #9428 fixed a significant issue with duplicate alarm IDs, which caused issues in how alarms were sent and displayed in Netdata Cloud.
This release also contains a few additional bug fixes that were not fully reviewed before the release of v1.23.0.
June 24, 2020 - Netdata v1.23.0 released!
The v1.23.0 release of the Netdata Agent is all about unlocking new depths of visibility for your applications, services, and systems. We have Kubernetes service discovery, new eBPF metrics like virtual filesystem switch and bandwidth per process out of the Linux kernel at event frequency, more interoperability with your monitoring stack thanks to a new exporting engine, and much more.
This release contains 2 new collectors, 1 new exporting connector, 1 new alarm notification method, 55 improvements, 45 documentation updates, and 40 bug fixes.
Our service discovery collector detects Kubernetes (k8s) pods
and immediately collects metrics from 22 different services as the associated pods are created, destroyed, and
scaled. Service discovery is installed when you use our Helm chart, which means
you can now collect and visualize service-, pod-, Kubelet-, kube-proxy-, and node-level k8s metrics with one helm install command and zero configuration. All our Kubernetes monitoring components are open source and free for clusters
of any size.
Our low-level Linux kernel monitoring via eBPF is now
supercharged. Thanks to an integration with
apps.plugin, you can now monitor how a specific
application interacts with the Linux kernel. This update also includes new metrics, such as virtual filesystem switch,
bandwidth per process, and much more. Netdata collects these metrics at an event frequency, even better than our famous
1s granularity, so that you can debug applications or anomalies with pinpoint accuracy. The eBPF collector is also now
installed and enabled by default except on static
builds.
Read our guide on troubleshooting apps with eBPF metrics for more details.
Netdata is now more interoperable with your existing monitoring stack thanks to the exporting engine, which replaces the backends system. You can now export to multiple external databases through Graphite, Google Cloud Pub/Sub, Prometheus remote write, MongoDB, and JSON connectors, plus others. Send metrics as soon as they're collected to enrich single pane of glass views or analyze Netdata's metrics with machine learning.
Read our guide on exporting metrics to Graphite for specifics on just one of many pipelines you can set up to archive your Netdata metrics.
We're also releasing an improvement for the availability of your monitoring and metrics: persistent metadata. The Agent now writes metadata to disk alongside metrics to allow access to non-active charts from Netdata Cloud and enable future features.
We added some enhancements to our documentation site, including a new guides section. We'll continue to populate with more use case- and scenario-based content to help you monitor, troubleshoot, visualize, and export your Netdata metrics.
See more news and previous releases at our blog or our releases page.
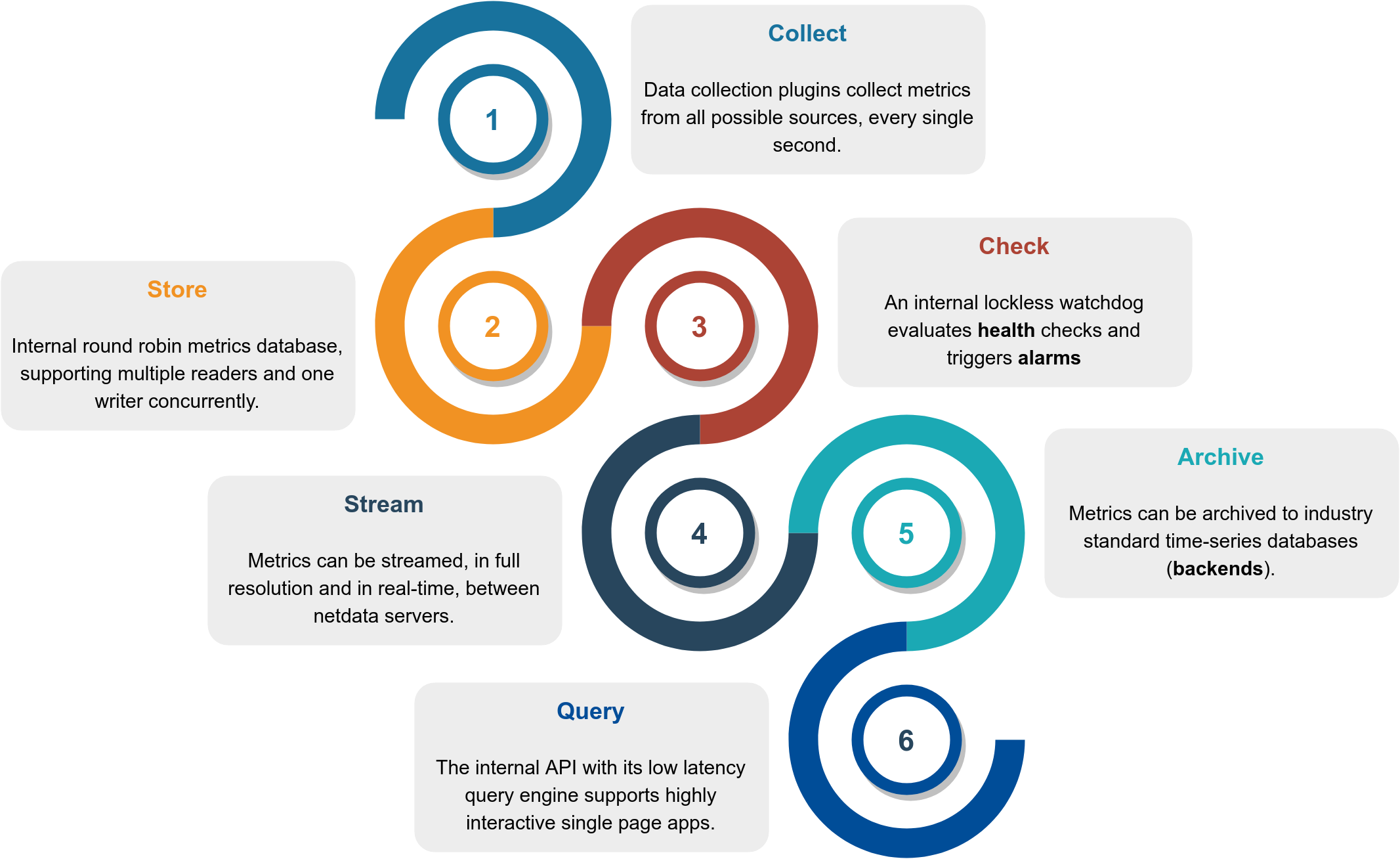
How it works
Netdata is a highly efficient, highly modular, metrics management engine. Its lockless design makes it ideal for concurrent operations on the metrics.
This is how it works:
| Function | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Collect | Multiple independent data collection workers are collecting metrics from their sources using the optimal protocol for each application and push the metrics to the database. Each data collection worker has lockless write access to the metrics it collects. | collectors |
| Store | Metrics are first stored in RAM in a custom database engine that then "spills" historical metrics to disk for efficient long-term metrics storage. | database |
| Check | A lockless independent watchdog is evaluating health checks on the collected metrics, triggers alarms, maintains a health transaction log and dispatches alarm notifications. | health |
| Stream | A lockless independent worker is streaming metrics, in full detail and in real-time, to remote Netdata servers, as soon as they are collected. | streaming |
| Archive | A lockless independent worker is down-sampling the metrics and pushes them to backend time-series databases. | exporting |
| Query | Multiple independent workers are attached to the internal web server, servicing API requests, including data queries. | web/api |
The result is a highly efficient, low-latency system, supporting multiple readers and one writer on each metric.
Infographic
This is a high level overview of Netdata feature set and architecture. Click it to to interact with it (it has direct links to our documentation).
Features
This is what you should expect from Netdata:
General
- 1s granularity - The highest possible resolution for all metrics.
- Unlimited metrics - Netdata collects all the available metrics—the more, the better.
- 1% CPU utilization of a single core - It's unbelievably optimized.
- A few MB of RAM - The highly-efficient database engine stores per-second metrics in RAM and then "spills" historical metrics to disk long-term storage.
- Minimal disk I/O - While running, Netdata only writes historical metrics and reads
errorandaccesslogs. - Zero configuration - Netdata auto-detects everything, and can collect up to 10,000 metrics per server out of the box.
- Zero maintenance - You just run it. Netdata does the rest.
- Zero dependencies - Netdata runs a custom web server for its static web files and its web API (though its plugins may require additional libraries, depending on the applications monitored).
- Scales to infinity - You can install it on all your servers, containers, VMs, and IoT devices. Metrics are not centralized by default, so there is no limit.
- Several operating modes - Autonomous host monitoring (the default), headless data collector, forwarding proxy, store and forward proxy, central multi-host monitoring, in all possible configurations. Each node may have different metrics retention policies and run with or without health monitoring.
Health Monitoring & Alarms
- Sophisticated alerting - Netdata comes with hundreds of alarms out of the box! It supports dynamic thresholds, hysteresis, alarm templates, multiple role-based notification methods, and more.
- Notifications: alerta.io, amazon sns, discordapp.com, email, flock.com, hangouts, irc, kavenegar.com, messagebird.com, pagerduty.com, prowl, pushbullet.com, pushover.net, rocket.chat, slack.com, smstools3, syslog, telegram.org, twilio.com, web and custom notifications.
Integrations
- Time-series databases - Netdata can archive its metrics to Graphite, OpenTSDB, Prometheus, AWS Kinesis, MongoDB, JSON document DBs, in the same or lower resolution (lower: to prevent it from congesting these servers due to the amount of data collected). Netdata also supports Prometheus remote write API, which allows storing metrics to Elasticsearch, Gnocchi, InfluxDB, Kafka, PostgreSQL/TimescaleDB, Splunk, VictoriaMetrics and a lot of other storage providers.
Visualization
- Stunning interactive dashboards - Our dashboard is mouse-, touchpad-, and touch-screen friendly in 2 themes:
slate(dark) andwhite. - Amazingly fast visualization - Even on low-end hardware, the dashboard responds to all queries in less than 1 ms per metric.
- Visual anomaly detection - Our UI/UX emphasizes the relationships between charts so you can better detect anomalies visually.
- Embeddable - Charts can be embedded on your web pages, wikis and blogs. You can even use Atlassian's Confluence as a monitoring dashboard.
- Customizable - You can build custom dashboards using simple HTML. No JavaScript needed!
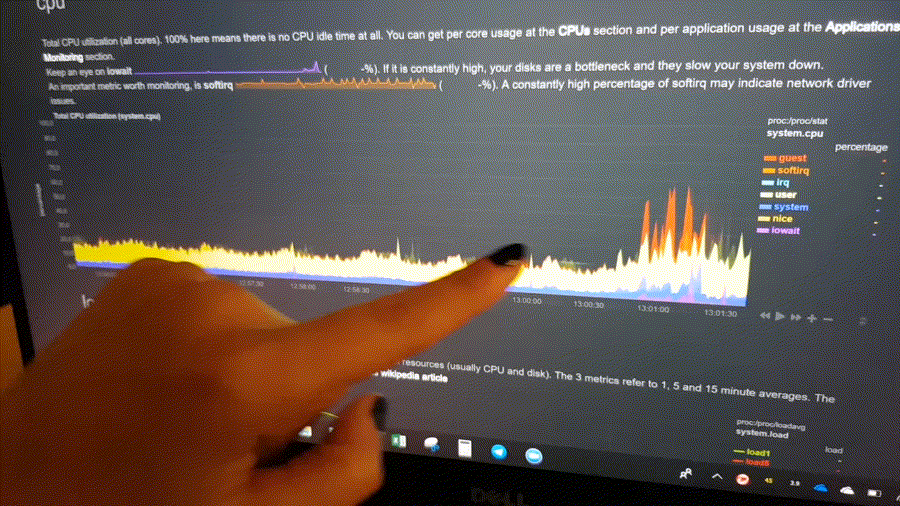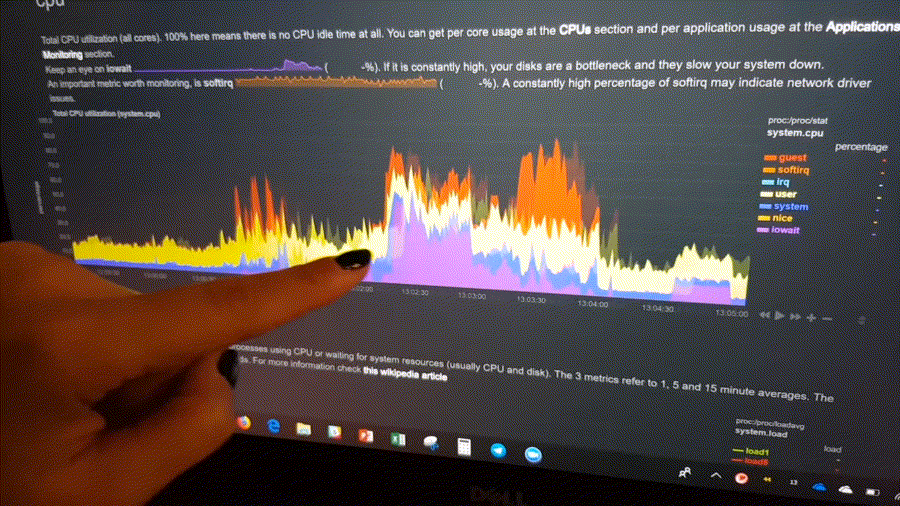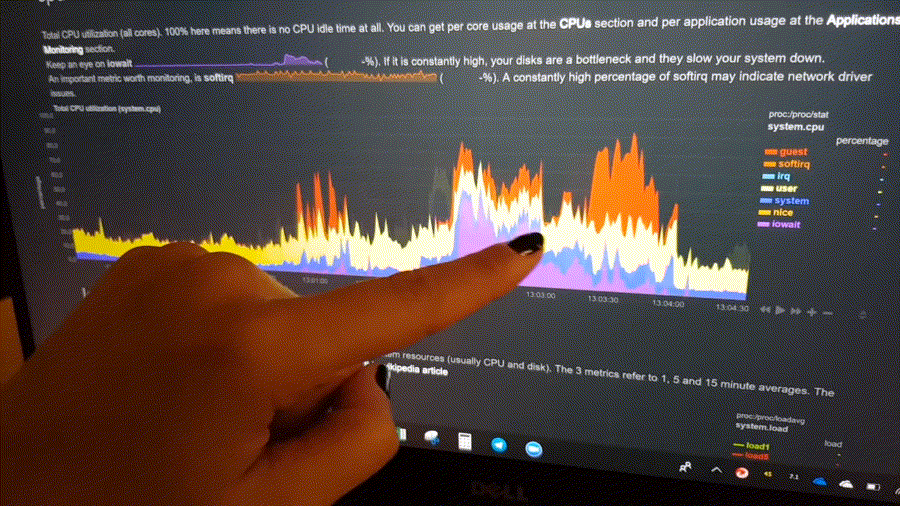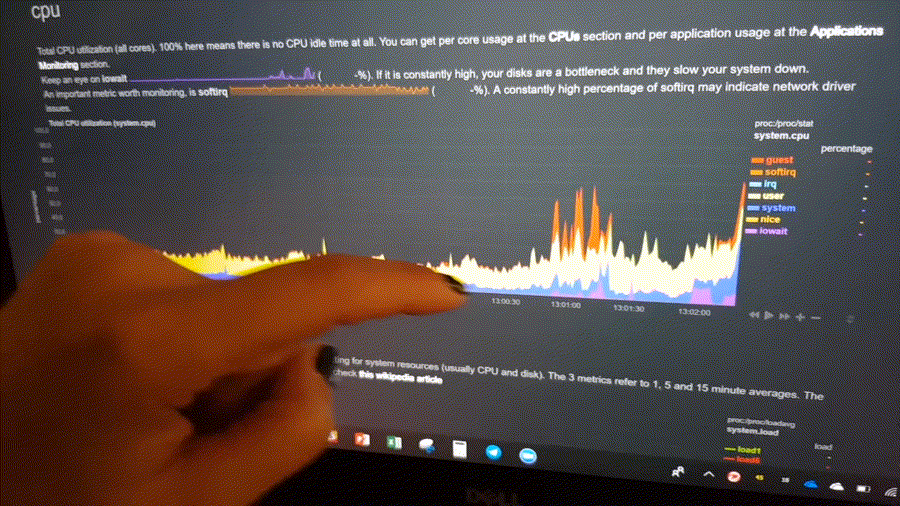
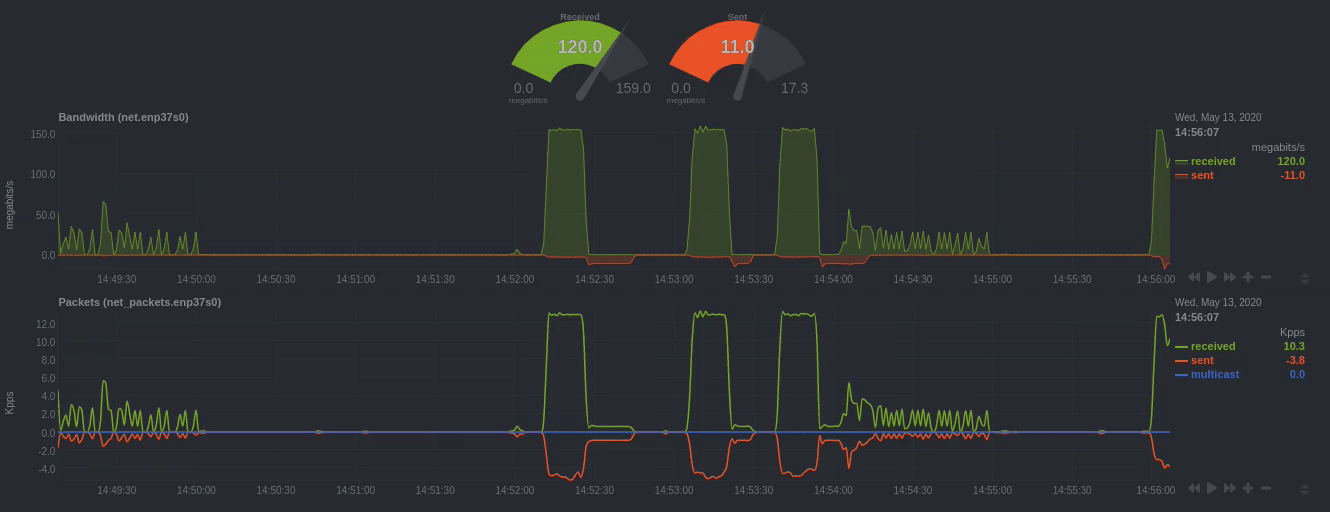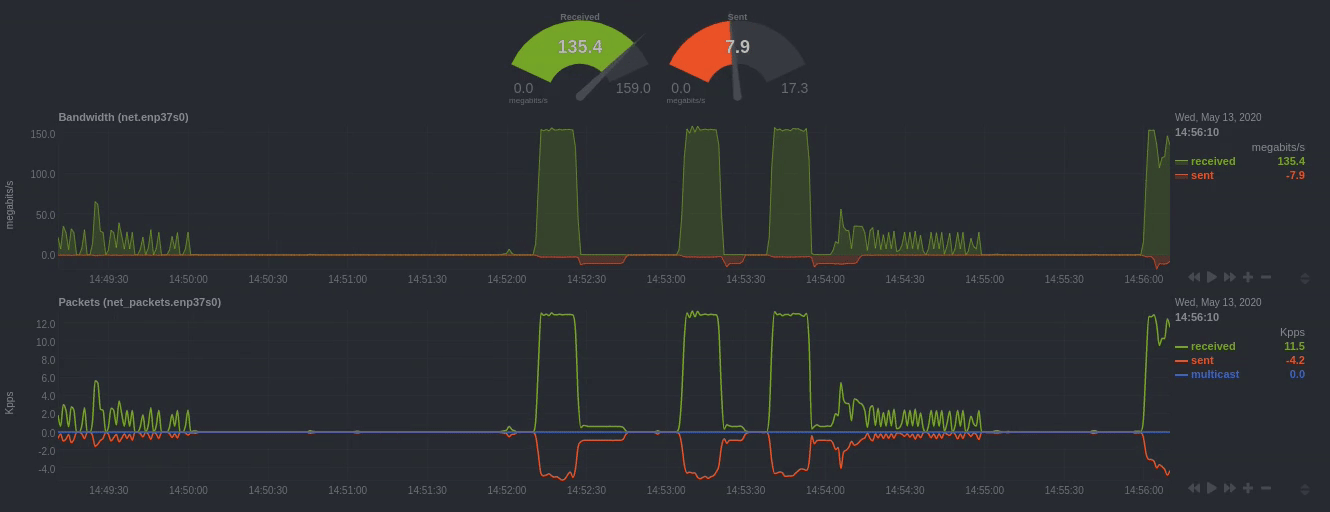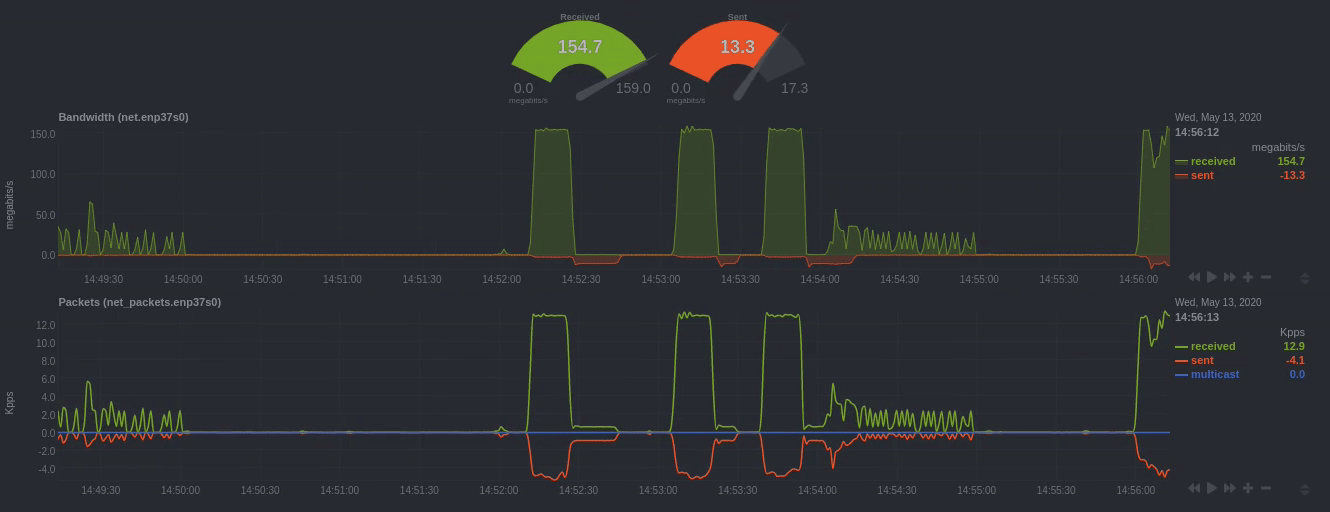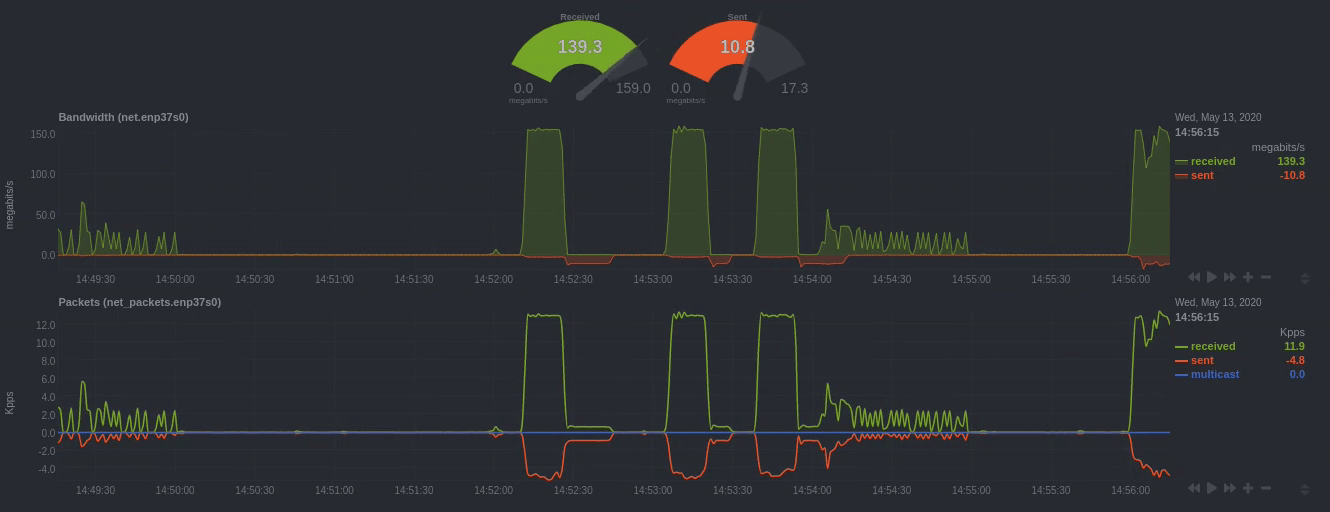
Positive and negative values
To improve clarity on charts, Netdata dashboards present positive values for metrics representing read, input,
inbound, received and negative values for metrics representing write, output, outbound, sent.
Netdata charts showing the bandwidth and packets of a network interface. received is positive and sent is
negative.
Autoscaled y-axis
Netdata charts automatically zoom vertically, to visualize the variation of each metric within the visible time-frame.
A zero-based stacked chart, automatically switches to an auto-scaled area chart when a single dimension is
selected.
Charts are synchronized
Charts on Netdata dashboards are synchronized to each other. There is no master chart. Any chart can be panned or zoomed at any time, and all other charts will follow.
Charts are panned by dragging them with the mouse. Charts can be zoomed in/out withSHIFT + mouse wheel while the
mouse pointer is over a chart.
Highlighted time-frame
To improve visual anomaly detection across charts, the user can highlight a time-frame (by pressing Alt + mouse selection) on all charts.
A highlighted time-frame can be given by pressing Alt + mouse selection on any chart. Netdata will highlight the
same range on all charts.
What Netdata monitors
Netdata can collect metrics from 200+ popular services and applications, on top of dozens of system-related metrics jocs, such as CPU, memory, disks, filesystems, networking, and more. We call these collectors, and they're managed by plugins, which support a variety of programming languages, including Go and Python.
Popular collectors include Nginx, Apache, MySQL, statsd, cgroups (containers, Docker, Kubernetes,
LXC, and more), Traefik, web server access.log files, and much more.
See the full list of supported collectors.
Netdata's data collection is extensible, which means you can monitor anything you can get a metric for. You can even write a collector for your custom application using our plugin API.
Documentation
The Netdata documentation is at https://docs.netdata.cloud, but you can also find each page inside of Netdata's
repository itself in Markdown (.md) files. You can find all our documentation by navigating the repository.
Here is a quick list of notable documents:
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
installer |
Instructions to install Netdata on your systems. |
docker |
Instructions to install Netdata using docker. |
daemon |
Information about the Netdata daemon and its configuration. |
collectors |
Information about data collection plugins. |
health |
How Netdata's health monitoring works, how to create your own alarms and how to configure alarm notification methods. |
streaming |
How to build hierarchies of Netdata servers, by streaming metrics between them. |
exporting |
Long term archiving of metrics to industry-standard time-series databases, like prometheus, graphite, opentsdb. |
web/api |
Learn how to query the Netdata API and the queries it supports. |
web/api/badges |
Learn how to generate badges (SVG images) from live data. |
web/gui/custom |
Learn how to create custom Netdata dashboards. |
web/gui/confluence |
Learn how to create Netdata dashboards on Atlassian's Confluence. |
You can also check all the other directories. Most of them have plenty of documentation.
Community
We recently launched the Netdata Community. You can find most of us there! It's also a good place to ask questions, find resources, or learn what features or fixes we are working on next.
We welcome contributions. Feel free to join the team!
To report bugs or get help, use GitHub's issues.
You can also find Netdata on:
License
Netdata is GPLv3+.
Netdata re-distributes other open-source tools and libraries. Please check the third party licenses.
Is it any good?
Yes.
When people first hear about a new product, they frequently ask if it is any good. A Hacker News user remarked:
Note to self: Starting immediately, all raganwald projects will have a “Is it any good?” section in the readme, and the answer shall be “yes.".
So, we follow the tradition...
Is it awesome?
These people seem to like it.